Braille code or symbols are formed within a space that contains six dots placed in two parallel lines each with three dots.
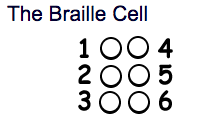
Variations in the placement of the raised dots are used to form the symbol such as a letter, number, or word. Combinations of Braille cells can also create mathematical signs or musical notes.
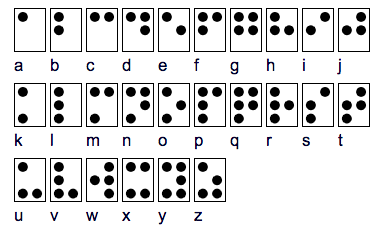
Many foreign languages, mathematics, music, and computers use Braille. It has many traditional features of languages such as capitalization and punctuation. Sometimes a single cell of six dots can even be used to write and read whole words such as "for", "and" or "the". Combinations of Braille cells can also represent mathematical symbols or music notes thus opening a world of information to the blind or those with low vision.
Quick Links:
Video: